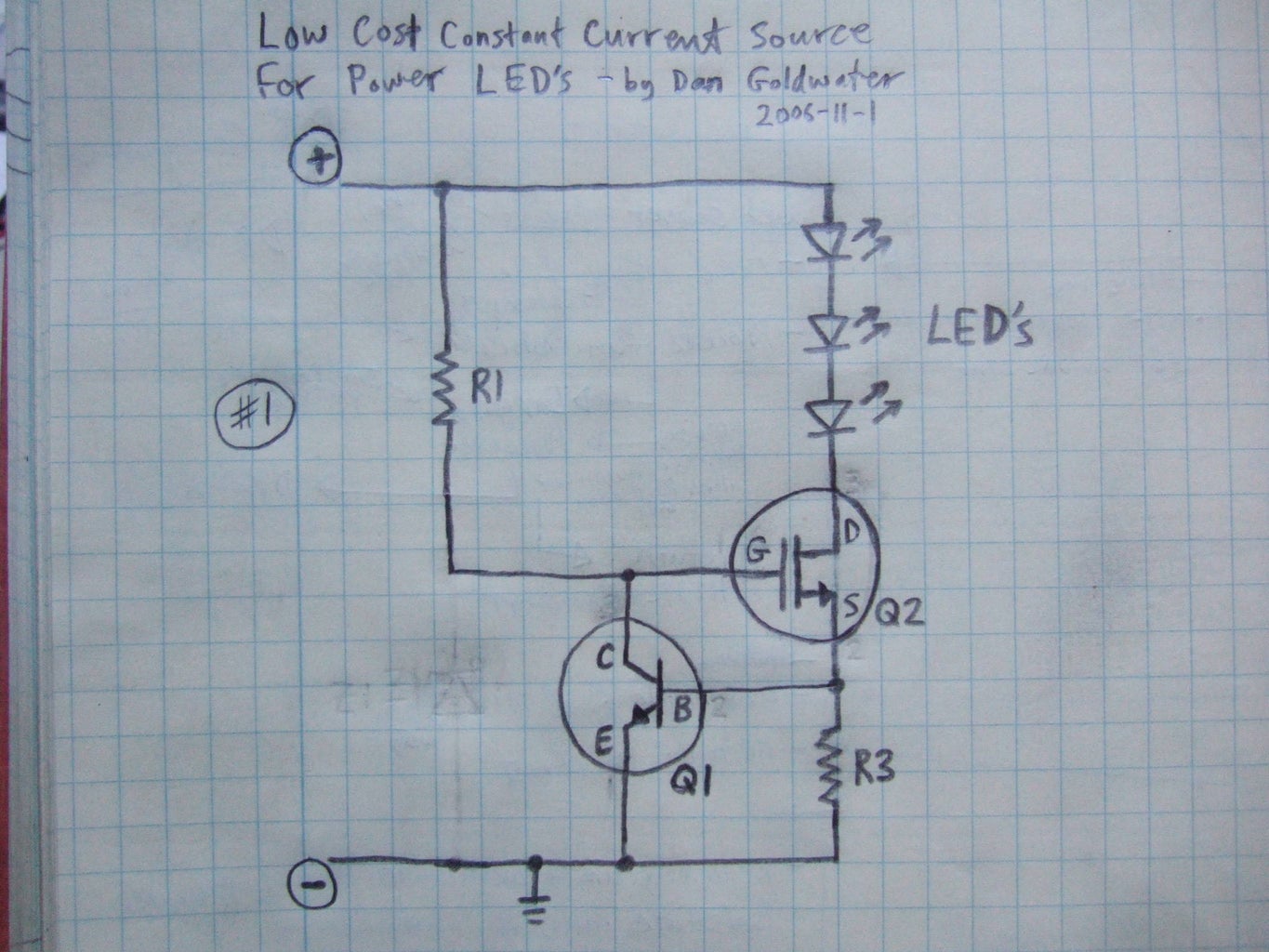
Design Optimization of an Efficient Circuit Diagram For best overall LED efficiency (which is your stated aim) you want high efficiency LEDs plus high efficiency drivers. There are many high power LED modules available, but they in many cases use LEDs that are less efficient than the best available. No amount of efficient driving of a very low efficiency LED will make up for its low efficiency Inductors: Inductors are used in LED driver circuits to store energy and smooth out the output voltage. When selecting inductors, look for those with a high saturation current rating and low DC resistance. Integrated Circuits: Many LED driver circuits use integrated circuits (ICs) for controlling the output voltage and current. When selecting

It is now time to design a driver to power them. This post goes through the calculations needed to design the circuit, the following post gives some recommendations on designing the PCB. Here is the final product. 26.4W Boost LED driver schematic 26.4W Boost LED driver PCB - 3D view It does all this with 80-95% power efficiency, no matter how much the step-down or step-up is. Pros: - consistent LED performance for a wide range of LED's and power supply - high efficiency, usually 80-90% for boost converters and 90-95% for buck converters - can power LED's from both lower or higher voltage supplies (step-up or step-down) In the above example circuit, the voltage source is a pure DC and the LED current set by the limiting resistor is 600mA. This gives a total LED power of 8.332W.The current limiting resistor is dissipating 3.67W.The total power applied to the circuit is 12W and the efficiency is only 69.43% which is very low.. LED Efficiency = 8.332W / 12W = 69.43%

High-efficiency LED driver circuit Circuit Diagram
Constant Current Driver: The driver ensures that the LED gets a constant current regardless of voltage fluctuations. This is ideal for LEDs that require a fixed current for proper operation. Constant Voltage Driver: The driver maintains a steady voltage but allows the current to fluctuate based on the load.This is typically used when the LED needs a specific voltage, regardless of the current The most efficient way to drive high-current LEDs is to use a DC-DC converter with current feedback. Commonalities among switching LED drivers. DC-DC converters are efficient power-conversion circuits that use passive, low-pass LC filters to smooth out switching action into constant voltages.

Power LED driver circuit diagrams can vary depending on the specific requirements of the LED lighting system. Some LED drivers are designed for high-power LEDs, while others are optimized for low-power or dimmable LEDs. The circuit diagram may also include additional features such as dimming control, thermal protection, and power factor correction. When driving LEDs at 1A, the obvious first choice to drive them is by using a switching LED driver circuit. An issue that arises with this approach is that at this high of power, switching drivers will only be able to drive a single strand each. That means we would require a lot of drivers on this board.